The Importance of Sweat: Functions and Consequences of the Lack of Sweating
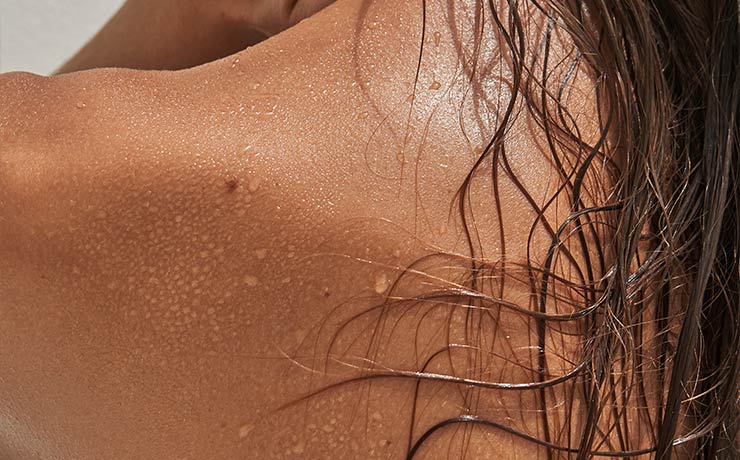
Sweating is a bodily function with more than one utility and today we will explain why we sweat. It may seem like a nuisance, since the smell or stains on clothes can create a social problem for the person who sweats a lot, but in reality it is essential for our lives to be able to sweat correctly.
What is sweat?
It is a liquid secreted by the sweat glands.
Types of sweat glands
There are different types of glands:
eccrine glands
They are glands distributed throughout the entire body, particularly abundant in the area of the soles of the feet, the armpits, the face and the palms of the hands. They are activated in childhood and continue to function throughout our lives.
apocrine glands
They are found in the armpits, perianal area, female labia majora, and areas of the male prepuce and scrotum, face, and scalp. They are activated in adolescence, when the production of hormones begins.
apoeccrine glands
They were recently discovered; its description was published in 1987, while the other two were already known at the end of the XIX-beginning of the XX century. They are only found in the armpits and their function is still not well known.
Sweat Functions
Sweat has more than one function in our body that explains why we sweat:
thermoregulation
Our body generates heat when we exercise and absorbs heat when we are exposed to a source of thermal energy (sun, fire, etc.). The heat generated, if we do not dissipate it, would raise our body temperature to levels incompatible with life. Transferring heat from our body to the sweat causes the sweat to evaporate and the body temperature to drop.
Acclimatization to warm temperatures
The composition of sweat changes as the ambient temperature rises or falls, avoiding excessive losses of sodium and chloride and reducing the risk of dehydration.
Maintenance of theskin barrier function**
Urea and lactate secreted by the eccrine glands are capable of retaining water, allowing the stratum corneum of the skin to remain hydrated.
antimicrobial defense
Recently, it has been described that some organic molecules present in sweat have a certain antibacterial capacity, which could be a defense role against the attack of pathogenic bacteria.
detoxification
This function has not yet been confirmed because studies demonstrating it have significant methodological problems, but it cannot be ruled out either. It has been seen that sweat carries with it molecules that are metabolic waste such as urea, or molecules that we capture from the environment and are pollutants instead of nutrients such as ethanol (intense sweating is also a symptom of a hangover), heavy metals or bisphenol A. The impact that this secretion has on our health remains to be defined.
Importance of Thermoregulation
But of all the functions mentioned, the most important is thermoregulation.
What happens if we don't sweat?
Some situations can reduce our ability to sweat: it happens with some medications (eg tricyclic antidepressants, some antipsychotics), with some health problems (ichthyosis, multiple sclerosis) or when damage to the skin of different etiology occurs (radiation, burns ).
Conditions that decrease sweating
Medicines
Some medications like tricyclic antidepressants and some antipsychotics can decrease our ability to sweat.
Health problems
Some health problems like ichthyosis and multiple sclerosis can decrease our ability to sweat.
skin damage
When skin damage of different etiology occurs (radiation, burns), our ability to sweat may decrease.
Sweating less than necessary, or even not being able to sweat, leads to heat intolerance. People suffering from hypohidrosis or anhidrosis can suffer from heat stroke, since poor thermoregulation allows body temperature to reach 40ºC or more. These temperatures cause damage to the brain, muscles and internal organs, even causing death. Finding a “plan B” to facilitate thermoregulation, such as spraying yourself regularly with a water spray or avoiding exposure to heat sources, is essential in these cases. It is also important to treat the cause of hypohidrosis, where possible.
Conclusion
As you can see, sweat is essential for our good health. Although it may seem like a nuisance, it is actually vital to our survival and well-being. So next time you're working up a sweat, remember that your body is doing exactly what it's supposed to to stay cool, hydrated and healthy.
Frequent questions
-
What is sweat? Sweat is a liquid secreted by the sweat glands in our body.
-
What are the functions of sweat? Sweat performs several functions in our body, including thermoregulation, acclimatization to hot temperatures, maintenance of the skin's barrier function, antimicrobial defense, and possibly detoxification.
-
What happens if we don't sweat? If we don't sweat, we can suffer from heat intolerance and risk heat stroke, which can be fatal.
-
What conditions can decrease our ability to sweat? Some medications, health problems, and skin damage can decrease our ability to sweat.
-
How can we facilitate thermoregulation if we cannot sweat? We can spray ourselves regularly with a water spray or avoid exposing ourselves to heat sources. It is also important to treat the cause of hypohidrosis, where possible.