Food intolerance or allergy: how to identify them and what role do genes play in this process?
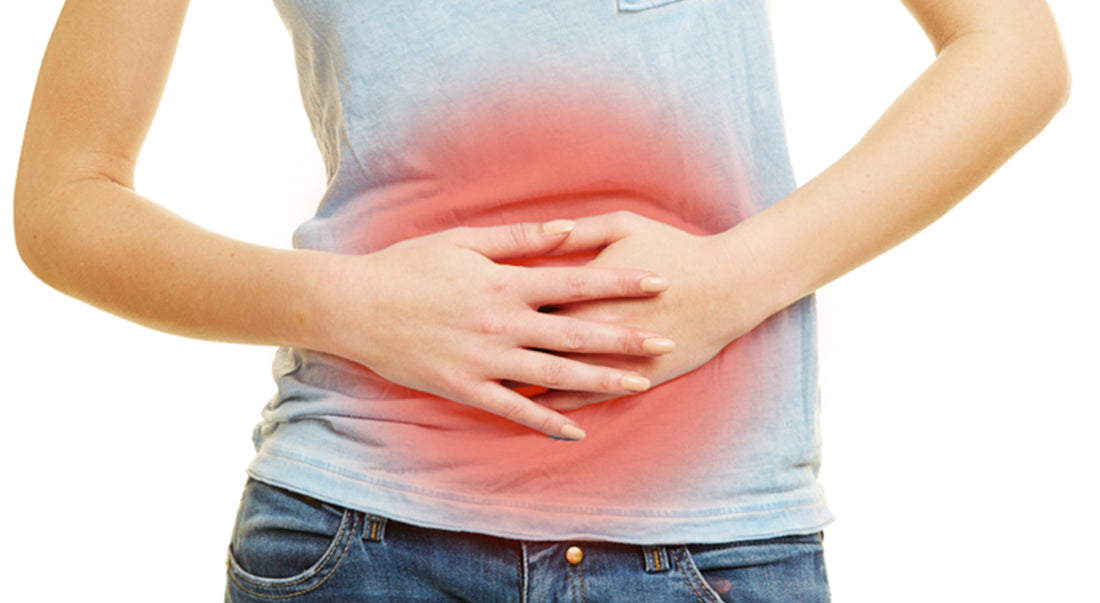
Have you felt bad after eating a dish that you used to love? You may suffer from a food intolerance or allergy, which means that your body is not prepared for any of the substances present in the food. It is important to pay attention to these symptoms, since a food intolerance or allergy can significantly affect your quality of life.
There are three types of food intolerance: enzymatic or metabolic intolerance, pharmacological or clinical intolerance, and intolerance due to an undetermined cause.
Enzyme intolerance occurs when your body is unable to metabolize a substance you are ingesting because one of the enzymes involved in its breakdown is not produced or is inefficient. Common examples are lactose intolerance and hereditary fructose intolerance.
Pharmacological or clinical intolerance occurs when your body reacts abnormally to a substance, as occurs in histamine intolerance.
Intolerance due to undetermined cause is more difficult to identify, but can occur with additives in processed dishes.
On the other hand, food allergies occur when the immune system overresponds to food molecules. A common example is a peanut allergy. It is important to identify if you suffer from food intolerance or allergy to avoid health complications.
It should be noted that genes can influence this process. For example, in the case of lactose intolerance, some genes may influence the production of the enzyme lactase, which is necessary to break down lactose. That is why the genetic test can be useful to identify if you have a predisposition to suffer from any food intolerance.
In conclusion, if you feel sick after eating a food, do not ignore these symptoms. Identifying if you suffer from food intolerance or allergy can help you improve your quality of life and prevent health complications. Also, keep in mind that genes can influence this process, so a genetic test can be a useful tool to discover your genetic predispositions.