Types of eczema on the skin and tips to treat them
Introduction
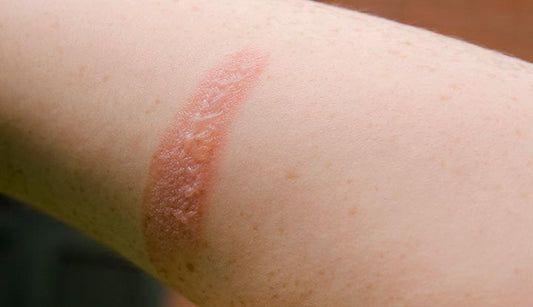
Eczema is a skin condition that causes redness, itching, inflammation, and sometimes blistering and scabbing. Although it can be difficult to treat, there are several types of eczema and various treatment options to alleviate its symptoms. In this article, we'll explore the different types of eczema and share helpful tips for treating them.
types of eczema
atopic eczema
Atopic eczema is the most common form of eczema and usually appears in childhood. It is characterized by outbreaks of inflammation, itching and dry skin. The exact cause of atopic eczema is unknown, but it appears to be related to genetic and environmental factors.
contact eczema
Contact eczema occurs when the skin comes into contact with an irritant or allergenic substance, such as chemicals, detergents, metals, or plants. The skin can become red, swollen, and itchy. The best way to treat contact eczema is to identify and avoid the responsible allergen or irritant.
Seborrheic eczema
Seborrheic eczema is a chronic skin condition that causes yellowish, greasy scales to appear in areas where there is increased sebum production, such as the scalp, face, and chest. It may be related to the presence of yeasts of the genus Malassezia on the skin.
nummular eczema
Nummular eczema is characterized by the appearance of coin-shaped, red, and crusty lesions. It is more common in older adults and may be related to dry skin or a response to a skin injury, such as an insect bite or burn.
dyshidrotic eczema
Dyshidrotic eczema primarily affects the hands and feet, causing small, itchy, swollen fluid-filled blisters. It may be related to factors such as stress, allergies, and exposure to irritants.
Tips to treat eczema
Identify and avoid triggers
The first step in treating eczema is to identify and avoid the triggers. These can vary depending on the type of eczema and the individual, and include chemical irritants, allergens, temperature changes, stress, and certain foods.
Keep skin hydrated
emollient creams
Keeping the skin hydrated is critical to relieving the dryness, itchiness, and inflammation associated with eczema. Emollient creams are moisturizing products that help retain moisture in the skin and restore the skin barrier. Apply emollients several times a day, especially after bathing.
lukewarm baths
Warm baths with water that is not too hot can help to hydrate the skin and relieve itching. Avoid using harsh soaps, and add bath oils or Epsom salts to the water to increase hydration.
Medical treatments
topical corticosteroids
Topical corticosteroids are anti-inflammatory medications that are applied directly to the skin to reduce inflammation and itching. These treatments can be effective in controlling the symptoms of eczema, but they should be used with caution and under medical supervision, as they can have side effects.
Calcineurin inhibitors
Calcineurin inhibitors, such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, are topical medications that reduce inflammation and itching by inhibiting an enzyme involved in the skin's immune response. These treatments may be an option for those who cannot use topical corticosteroids or for sensitive areas of the skin, such as the face.
Phototherapy
Phototherapy involves controlled exposure of the skin to ultraviolet (UV) light and can be effective in treating some types of eczema, such as atopic eczema. Phototherapy must be performed under medical supervision and may require several sessions to obtain results.
Home Treatments
Aloe vera
Aloe vera gel has anti-inflammatory and soothing properties that can help relieve the itching and inflammation of eczema. Apply the gel directly to the affected areas several times a day.
Coconut oil
Coconut oil is a natural moisturizer that can help soothe dry, itchy skin associated with eczema. Apply coconut oil directly to the affected skin several times a day, especially after bathing.
Apple cider vinegar
Apple cider vinegar has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties that can help treat eczema. Dilute one part apple cider vinegar with one part water and apply the solution to the affected areas with a cotton ball. Do not apply undiluted vinegar, as it can irritate the skin.
Conclusion
Eczema is a skin condition that can be difficult to manage, but by knowing the different types of eczema and following the right advice, it is possible to control and alleviate your symptoms. Identifying and avoiding triggers, keeping skin hydrated, and using medical treatments and home remedies can significantly improve the quality of life for people with eczema.
Frequent questions
-
What is the cause of eczema? The exact cause of eczema is not known, but it is believed to be related to a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
-
Is eczema contagious? No, eczema is not a contagious disease and cannot be passed from one person to another.
-
How long does an eczema flare-up last? The duration of an eczema flare-up can vary depending on the type of eczema and the individual. Some outbreaks may only last a few days, while others may persist for weeks or months.
-
Can eczema be cured? There is no definitive cure for eczema, but its symptoms can be controlled and alleviated through proper management of the condition and adoption of skin care habits.
-
What foods can trigger eczema? Some foods that can trigger eczema include dairy, eggs, nuts, wheat, and soy. However, food triggers vary by individual, and not all eczema patients will experience problems with the same foods.